Natural teeth and alveolar bone are bonded by periodontal ligament, while
dental implants and alveolar bone are directly osseous bonds. Because of different bonding modes, there are significant differences in mechanical properties between them. In normal operation, the stress of natural teeth is transferred to alveolar bone through periodontal ligament. When the implant is implanted into jaw bone, it forms a whole structure with surrounding bone. Under functional condition, it bears load, and distributes and transmits occlusal force.
|
Comparison of mechanical points between natural teeth and implant teeth
|
|
|
Natural teeth
|
Teeth Implants
|
|
Connection with alveola
bone
|
Periodontal ligament
|
Synostosis
|
|
Receptor
|
Periodontal mechanoreceptor
|
Osteoreceptor
|
|
Susceptibility
|
High
|
Low
|
|
Range of motion
|
20~100um
|
3~5um
|
|
Mode of motion
|
Immediate motion, progressive
motion
|
Progressive motion
|
|
Stage of motion
|
Nonlinear and complex
Linear and elastic
|
Linear and elastic
|
|
Fulcrum of lateral force
|
Root 1/3
|
Cervical cortex
|
|
Characteristic of Load Bearing
|
Fast absorption and occlusal force dispersion
|
Stress concentrates on the cortex of bone
|
|
Clinical manifestations after overload
|
Ache, widening of periodontal ligament and
loosening of teeth
|
Screw loosening or breaking,
prosthesis and abutment loosening,implant breaking, bone resorption
|
|
Functional occlusal force
|
Low,andhigh degree of control
|
High, low degree of control
|
|
Modulus of elasticity
|
Close to bone tissue
|
Nearly 10 times higher than bone
tissue
|
|
Stress Distribution Characteristics
|
Mainly in periodontal support tissue
|
Mainly on the crest of the
alveolar ridge in the neck of the implant
|
|
Degree of motion
|
Physiokinetics
|
No physiokinetics
|
|
Orthodontic movement
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
When subjected to impact
|
It can cushion the impact
|
It cannot cushion the impact.
|

 +86-021-50327060
+86-021-50327060
 zq@lzqtech.com
zq@lzqtech.com
 Medical Instrument
We can achieve perfect edge quality and dimensional tolerance up to±0.0005mm (±0.5μm) in the process of micro, ultra-long, ultra-thin, super-abrasive, impact-resistant, high-precision and combined ... VIEW MORE
Medical Instrument
We can achieve perfect edge quality and dimensional tolerance up to±0.0005mm (±0.5μm) in the process of micro, ultra-long, ultra-thin, super-abrasive, impact-resistant, high-precision and combined ... VIEW MORE Implant
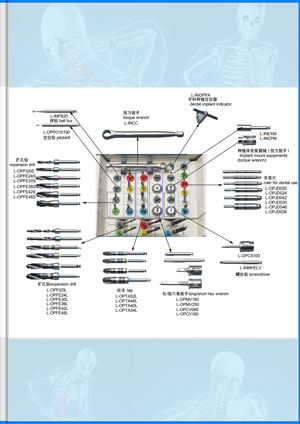
Corresponding and matching drills and tools of different types, forms, shapes, structures can be high precisely ground to mold according to different brands and different types of implants forms, shap... VIEW MORE
Implant
Corresponding and matching drills and tools of different types, forms, shapes, structures can be high precisely ground to mold according to different brands and different types of implants forms, shap... VIEW MORE Cutting Tools
Super-hardness machining for special, non-standard new ite ms with different size and tolerance. VIEW MORE
Cutting Tools
Super-hardness machining for special, non-standard new ite ms with different size and tolerance. VIEW MORE Accessory Parts
we can customize for you according to your samples or drawings for any manufacturing of ceramic,carbide,stainless high-speed steel, stainless steel, titanium alloy, titanium diamond, etc series, hig... VIEW MORE
Accessory Parts
we can customize for you according to your samples or drawings for any manufacturing of ceramic,carbide,stainless high-speed steel, stainless steel, titanium alloy, titanium diamond, etc series, hig... VIEW MORE

 +86-021-50327060
+86-021-50327060 
 NO.1269 Plant, Jinhu Road, Jinqiao Export Processing Zone, Pudong New District, Shanghai, China.
NO.1269 Plant, Jinhu Road, Jinqiao Export Processing Zone, Pudong New District, Shanghai, China. 
